Follow the steps below to Create a New Linux Virtual Machine running SQL Server Engine and Execute Queries using SQLCMD Tool.
Microsoft Azure Cloud provides Linux VM images that have SQL Server vNext included.

Step 1: Microsoft Azure Marketplace: Search for Image
Search for SQL Server vNext on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.2
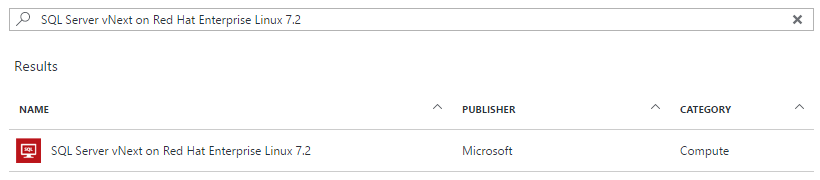

Step 2: Microsoft Azure: Create the Linux Virtual Machine:
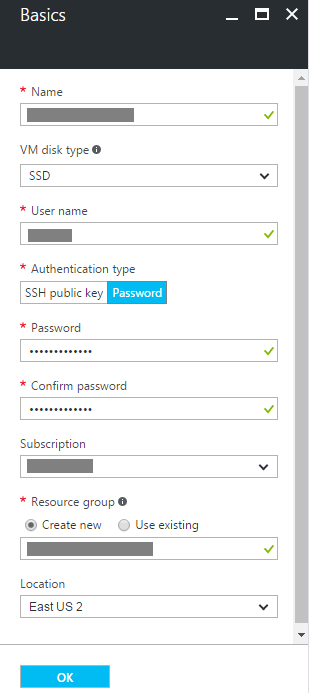
Step 3: Microsoft Azure: Create the Linux Virtual Machine: Choose Size
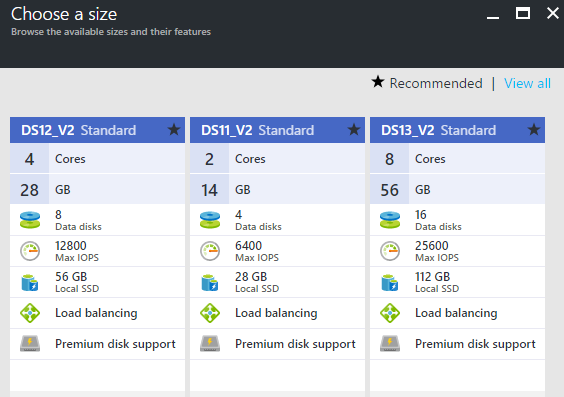
Step 4 Microsoft Azure: Create the Linux Virtual Machine: Security Rule
To remotely connect to SQL Server on an Azure VM, you must configure an inbound rule on the network security group.
Step 5: PuTTY: SSH to Linux Virtual Machine running in Microsoft Azure:
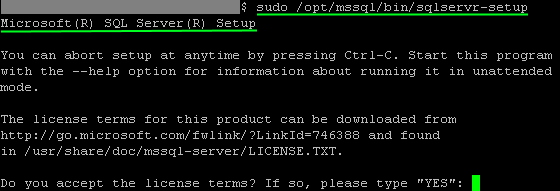
Step 6: Setup & Configure SQL Server:
Execute this Linux command to setup SQL Server: sudo /opt/mssql/bin/sqlservr-setup:
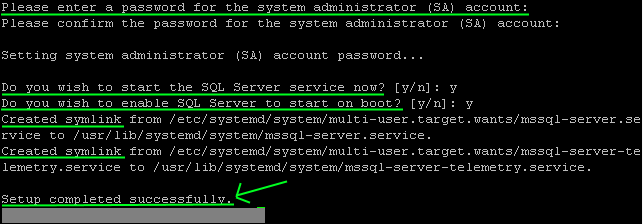
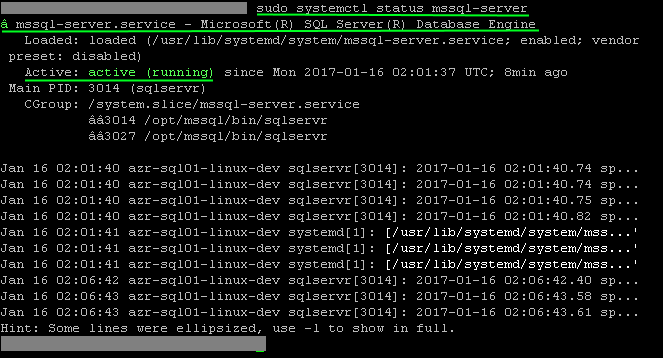
Step 7: Check status of SQL Server service:
Execute this Linux command to check service status: sudo systemctl status mssql-server:
Step 8: Download mssql-tools, update & create a symlink:
Execute this Linux command to download the Microsoft Red Hat repository configuration file.:
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/7/prod.repo > /etc/yum.repos.d/msprod.repo

Execute these Linux commands to install mssql-tools:
sudo yum update
sudo yum install mssql-tools unixODBC-utf16-devel
yum check-update
yum update mssql-tools
Execute this Linux command to create symlinks to SQLCMD under /usr/bin/:
ln -sfn /opt/mssql-tools/bin/sqlcmd-13.0.1.0 /usr/bin/sqlcmd
This fixes the issue with receiving an error when excuting SQLCMD:
-bash: sqlcmd: command not found
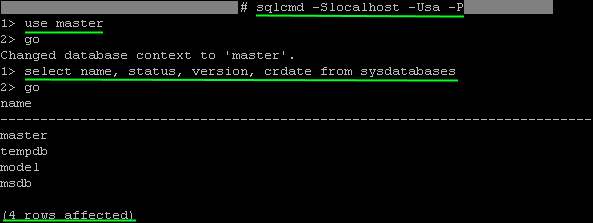
Step 9: Use SQLCMD to execute queries:
Execute this Linux command to connect to the local SQL Server instance (localhost):
sqlcmd -S localhost -U SA -P YourPassword
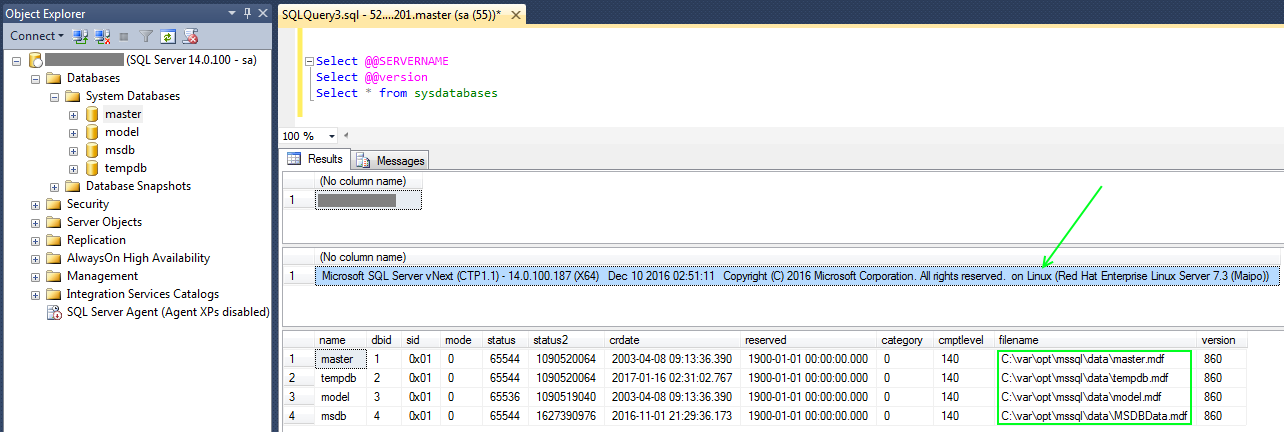
Step 10:Use SSMS to connect to Linux Virtual Machine:
Misc:
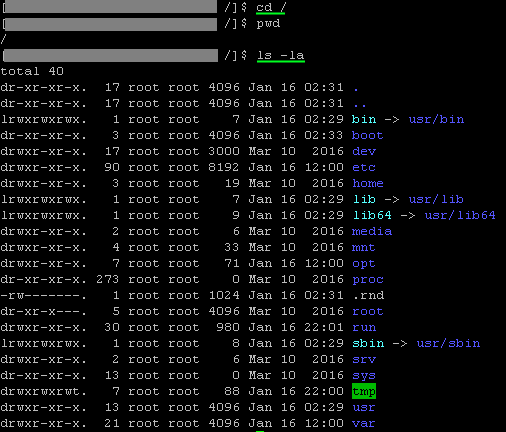
Execute this Linux command to take you to the entire system's root directory:
cd /
pwd
ls- la
Execute this Linux command to locate the SQL Server .mdf and .ldf files:
find / -name "opt"
cd /var/opt/mssql/data
ls -la
Execute this Linux command to locate the SQL Server binaries:
find / -name "opt"
cd /opt/mssql/bin
ls -la
Execute this Linux command to view the symlink:
cd /usr/bin
ls -la
Execute this Linux command to view the System Logs:
cd /var/log
ls
(See boot.log, yum.log, maillog)
Execute these Linux command to view system performance:
top
i.e. % CPU - if have 8 cores, then top can display from 0% (idle system) to 800% (All CPUs used & maxed)
vmstat
iostat
Resources:
Provision a Linux SQL Server VM in Azure
Install SQL Server tools on Linux
Connect and query SQL Server on Linux with sqlcmd
Use SSMS on Windows to connect to SQL Server on Linux
Troubleshoot SQL Server on Linux
Connecting with sqlcmd
Configure SQL Server on Linux with mssql-conf
Manage SQL Server on Linux
Linux Navigate Directories
Linux Virtual Machine Documentation
Linux Log Files
|
|
|
|
|
|