Solution:
Microsoft Azure - Traffic Manager Profile - EndPoints:
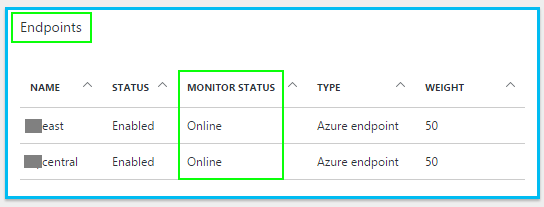
To obtain Azure Traffic Manager EndPoints Monitor Status you can use the below method which uses Powershell & Chrome Postman to submit a
call to Azure Service Management REST API.
Powershell - used to obtain a Bearer Token which is required for Azure SM REST API Header Authorization.
Chrome PostMan - used to submit the API call and get a response back indicating the Traffic Manager EndPoints Monitor Status.
Note: The Bearer Token from Powershell must be on a single-line. Use NotePad++..Edit..Line Operations..Join Lines if needed.
If not on a single-line you will likely see a 401 Invalid Token error.
Powershell:
Modify these two lines:
Out-File C:\Downloads\Powershell\bearerToken.txt
$adTenant = "InsertYourAzureActiveDirectoryTenantNameHere.onmicrosoft.com"
(You can obtain this from https://manage.windowsazure.com URL - after you log in. You need the value after @ and before # in the URL)
# Load ADAL Assemblies
$adal = "${env:ProgramFiles(x86)}\Microsoft SDKs\Azure\PowerShell\ServiceManagement\Azure\Services\Microsoft.IdentityModel.Clients.ActiveDirectory.dll"
$adalforms = "${env:ProgramFiles(x86)}\Microsoft SDKs\Azure\PowerShell\ServiceManagement\Azure\Services\Microsoft.IdentityModel.Clients.ActiveDirectory.WindowsForms.dll"
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadFrom($adal)
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadFrom($adalforms)
# Set Azure AD Tenant name
$adTenant = "InsertYourAzureActiveDirectoryTenantNameHere.onmicrosoft.com"
# Set well-known client ID for Azure PowerShell
$clientId = "1950a258-227b-4e31-a9cf-717495945fc2"
# Set redirect URI for Azure PowerShell
$redirectUri = "urn:ietf:wg:oauth:2.0:oob"
# Set Resource URI to Azure Service Management API
$resourceAppIdURI = "https://management.core.windows.net/"
# Set Authority to Azure AD Tenant
$authority = "https://login.windows.net/$adTenant"
# Create Authentication Context tied to Azure AD Tenant
$authContext = New-Object "Microsoft.IdentityModel.Clients.ActiveDirectory.AuthenticationContext" -ArgumentList $authority
# Acquire token
$authResult = $authContext.AcquireToken($resourceAppIdURI, $clientId, $redirectUri, "Auto")
# Create Authorization Header
$authHeader = $authResult.CreateAuthorizationHeader()
# Output the header value
Write-Host "Bearer Token: $authHeader"
$authHeader | Out-File C:\Downloads\Powershell\bearerToken.txt
Chrome Postman:
Once you have the Bearer Token from Powershell, launch Chrome PostMan App and configure the Headers Presets and include these two below:
Content-Type = application/json
Authorization = Bearer Token Value
Next, submit a call to the Azure Service Management REST API using GET. The below example gets the Traffic Manager EndPoints Monitor Status.
(You can get obtain your SubscriptionID from Powershell or https://resources.azure.com)
https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/InsertSubscriptionIDHere/resourceGroups/RG_TM_PRD/providers/Microsoft.Network/
trafficManagerProfiles/InsertTrafficManagerNameHere?api-version=2015-11-01
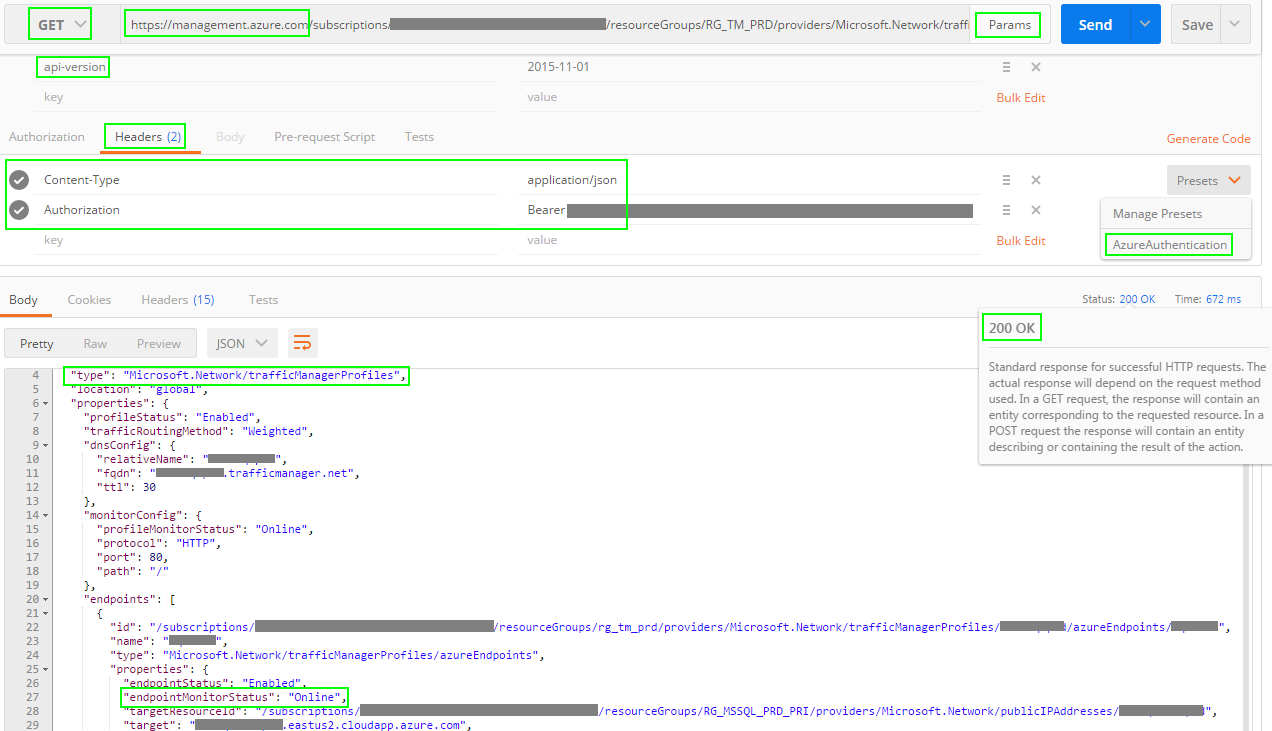
That's it! Now you have the Traffic Manager EndPoints Monitor Status via an authenticated REST API call.
Resources:
feedback.azure.com
Troubleshooting degraded state on Azure Traffic Manager
Setting up Postman to call the Azure Management APIs
Leveraging the Azure Service Management REST API with Azure Active Directory and PowerShell / List Azure Administrators
Postman
Errors from Secured Resources
Note:
The Bearer Token will expire with an error similar to below will be thrown. Just re-generate a new Bearer Token using
Powershell and update that value in Postman.
{
"error": {
"code": "ExpiredAuthenticationToken",
"message": "The access token expiry UTC time '3/16/2016 5:38:33 PM' is earlier than current UTC time '3/16/2016 5:47:28 PM'."
}
}
You can also check the Load Balancers directly:
http://azrcen.centralus.cloudapp.azure.com/
http://azreast.eastus2.cloudapp.azure.com/
|
|
|
|
|
|